Understanding the U.S. Deportation Process: A Closer Look at the Steps Involved
The U.S. deportation process is a tangled issue that has long been a subject of spirited debate and legal scrutiny. In our opinion, understanding how deportation works—and the financial, legal, and human costs involved—requires that we dig into the process step by step. This discussion explores everything from identifying who is removable to the challenges of a strained immigration court system, as well as the economic implications of detaining and removing individuals from U.S. soil.
What follows is our detailed breakdown of the U.S. deportation mechanism, accompanied by analysis of its tricky parts and the pressures it puts on both law enforcement agencies and the affected communities. We have organized our discussion under topical subheadings, sprinkled with relevant details, bullet lists, and tables where necessary.
How the U.S. Identifies Removable Individuals
The very first step in the deportation process is identifying who qualifies as “removable.” In practice, this involves an in-depth look at individual circumstances, such as visa overstay, illegal entry, and other definitions of being without legal status.
Criteria for Removal
The government considers several factors when deciding if someone is at risk, including:
- Entry method: Whether the individual entered the country legally or illegally
- Visa compliance: Overstays, violations of work or student visa conditions
- Criminal history: Any violation that might render a person “removable” even if they have not been convicted of a crime
- Changes in legal status: Revocations of programs or temporary status that previously protected them
Recent government actions have expanded the categories of removable individuals. For example, moves to end Temporary Protected Status for nationals from certain countries have expanded the net of those now vulnerable to removal. These changes reflect a broader shift towards enforcing immigration law more strictly and underscore the evolving nature of the legal criteria used.
Subtle Legal and Policy Shifts
Legal experts describe the policy shifts as a series of little details that compound the national debate on immigration. When programs change or expire, many individuals suddenly find themselves without a protective legal status. The changes can be nerve-racking for both legal practitioners and the affected communities, who must then figure a path through a system loaded with problems.
Step-by-Step: Arrests and Detentions in the Deportation Process
Once an individual is identified as removable, the process often starts with an arrest. This phase is filled with confusing bits and nerve-racking situations—especially since law enforcement agencies sometimes have very aggressive arrest quotas, which can complicate matters on the ground.
The Role of Federal Agencies
Since the early days of this policy shift, especially under administrations that seek a hard line on immigration, multiple federal agencies have been roped in to assist with arrests. These include:
- Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE): The frontline agency responsible for imposing arrest quotas and detentions.
- The FBI and U.S. Marshals: Often acting in support to meet aggressive targets.
- Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA): In some instances, the DEA has also been involved in arrests related to immigration enforcement.
Notably, while “at-large” arrests by federal agents catch headlines, local law enforcement remains responsible for the majority of the arrests. Local police’s involvement is typically facilitated by programs like the Criminal Alien Program and provisions such as 287(g), which allow local authorities to conduct limited immigration law enforcement tasks.
Detention Dynamics: A Costly and Contentious Issue
After being arrested, individuals may be taken into immigration detention—a stage that brings with it a host of complicated pieces. Detention means confinement until a final decision is made in immigration court, but the process is not only legally delicate; it is also hugely expensive. Public contracts with private prison operators can skyrocket costs, with some contracts potentially generating annual revenues in the hundreds of millions.
| Agency or Contractor | Role | Estimated Annual Cost/Revenue |
|---|---|---|
| ICE | Primary detention and enforcement | N/A |
| CoreCivic | Private prison operator | $180 million (estimate) |
| Other Contractors | Support detention infrastructure | Varies |
This table illustrates the stark economic realities behind a process that seems unnecessarily drawn-out and expensive.
Challenges and Delays in the Immigration Court System
Once detention is in play, the individual must face the immigration court system—a labyrinthine realm where legal proceedings are often laden with challenges and delays. The process involves multiple court appearances, each with its own set of confusing bits and delicate legal twists and turns.
Overburdened Courts and Massive Backlogs
One of the most critical issues in the deportation process is the burden on the immigration courts. With more than four million pending cases reported in recent times, the system remains under immense pressure. This backlog means that when someone is called to court, the waiting period might stretch for years—especially for asylum claims where each case is full of problems requiring careful review.
The Legal Rights at Stake
Before a judge can issue a removal order, an individual is entitled to a hearing. Despite this right, many immigrants face lengthy delays, missing the chance to secure legal representation which further complicates their ability to mount a defense. A missed hearing or filing error can trigger an automatic removal order—a final and decisive act that carries lifelong consequences.
Key Factors Influencing Court Decisions
- Length of residence: Those who have lived in the country for less than a year may find it easier to claim asylum. In contrast, those residing for longer periods face a different set of challenges.
- Family ties: Immigrants with U.S. citizen family members might gain additional considerations that delay deportation, though these rarely provide a firm pathway to legal status.
- Criminal records: Even minor criminal activity can tip the scales, leading to a judge deeming an individual removable.
It is these little details, these subtle parts of each case, that complicate the process. Without sufficient legal support, many people end up with orders of removal, some of which later prove to be administrative errors or subject to further appeals.
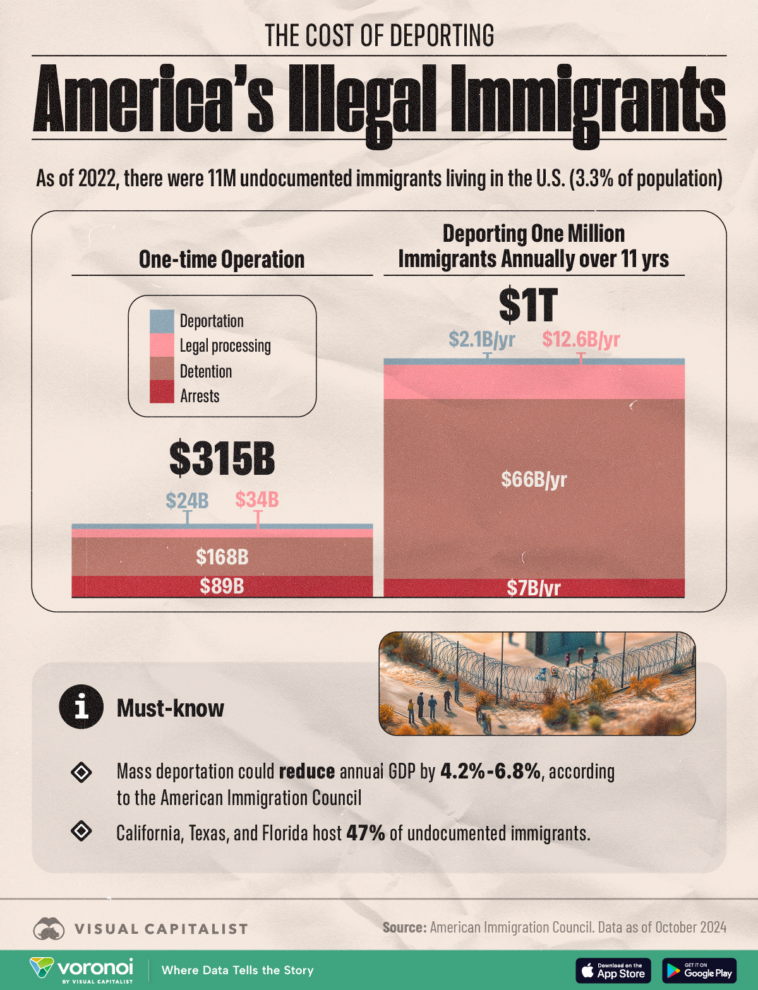
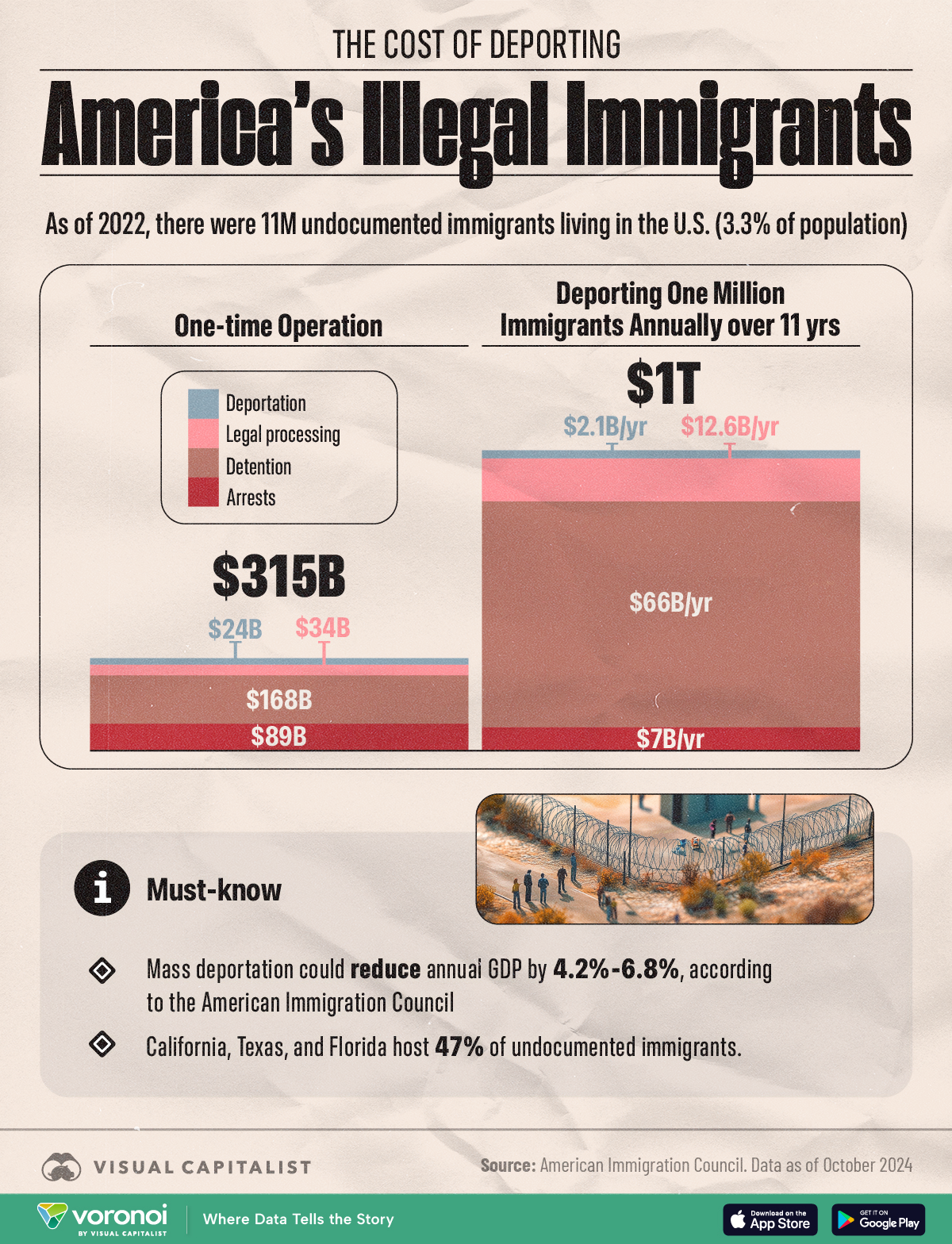
The Cost of Deportation: Financial Implications for the U.S. Government
Beyond the immediate human and legal challenges, the deportation process brings with it hefty costs. While the topic might seem intimidating at first, it is essential to take a closer look at how these expenses add up.
Budget Breakdown and Associated Expenses
Three major federal agencies are allocated specific budgets to cover their roles in immigration enforcement. These include:
- ICE: Approximately $8 billion
- Customs and Border Protection (CBP): Roughly $20 billion
- U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS): About $865 million, which is largely covered by application fees
Although not all of these funds are dedicated solely to enforcement activities, they represent a significant financial commitment. The reliance on government contracts with private entities for detention and processing can lead to even more spending. For example, a single contract with a private prison operator might generate over $180 million in annual revenue, underlining the high stakes involved in these operations.
Implications for Taxpayers and Policy Reform
The substantial costs associated with deportation have implications far beyond the courtroom. Taxpayers ultimately foot these bills, prompting questions about whether these resources might be better allocated with comprehensive law enforcement reforms. Legislative reform in the realm of immigration is not new—decades of attempts have struggled in Congress, stalled by political disagreements and intense public debates.
Potential Areas for Cost-Saving and Efficiency
- Modernizing detention facilities: Updating the infrastructure could reduce long-term costs.
- Investing in legal aid: Providing better access to legal representation might streamline court processes and reduce unnecessary deportations.
- Policy overhaul: Congress could help bring the process into the 21st century with reforms that address both enforcement and humanitarian concerns.
Ultimately, a more efficient system could potentially ease the financial burden on the government while also serving justice more fairly. However, achieving these improvements will require bipartisan cooperation and a willingness to tackle the system’s hidden complexities head-on.
The Reality Behind Expedited Removal and Its Legal Ramifications
An area of growing concern is the use of programs like expedited removal, where individuals can be deported quickly without a lengthy court process. While these measures are intended to streamline border security, they are also full of problematic twists and turns from a legal perspective.
How Expedited Removal Works
Expedited removal allows immigration officers to bypass some of the traditional steps in the process, targeting those who have been in the U.S. for less than two years without legal status. This can mean that an individual might find themselves removed without ever setting foot in a courtroom.
Due Process Concerns
This fast-tracked process is often seen as off-putting by legal experts because it can strip individuals of their right to a fair hearing. Critics argue that bypassing the immigration court system deprives people of the chance to argue their case, representing a serious departure from established legal principles.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
- Due process rights: There is a growing concern that expedited removal undermines the constitutional rights guaranteed to all residents.
- Potential for abuse: Without the scrutiny of a court hearing, decisions made under expedited removal are more susceptible to errors that might later require lengthy legal battles.
- Impact on communities: Quick removals can tear apart families and disrupt communities, leading to long-term social repercussions that extend beyond immediate legal concerns.
These fine points of the expedited removal process highlight the need for thoughtful policy reform that balances national security with the preservation of individual rights.
Legal Appeals and the Path to Final Removal Orders
Even after an individual is detained, the legal process is not over. For many, the fight continues in immigration court, where appeals can eventually lead to final orders of removal. The path from initial arrest to a conclusive legal decision is riddled with twists and turns that exemplify the challenges within the current system.
The Role of Immigration Courts
Immigration courts are tasked with the critical job of evaluating each case on its specific merits. However, the system is currently strained for resources, with over a million pending cases. As a result, many individuals are forced to wait an intimidatingly long time before receiving a fair hearing.
Appeals and the Board of Immigration Appeals
For those given a final removal order, there remains the option of filing an appeal with the Board of Immigration Appeals (BIA). The journey through the appeals process is both time-consuming and legally challenging, involving multiple layers of judicial review that can eventually reach circuit courts or even the Supreme Court in rare cases.
Charting the Appeals Process
| Stage | Description | Possible Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Hearing | An immigration judge reviews the case and issues a preliminary decision. | Order of removal or referral for further review. |
| Board of Immigration Appeals | An appeal to the BIA, which reviews the judge’s decision. | Confirmation, modification, or reversal of the decision. |
| Circuit Court / Supreme Court | In rare cases, further appeals may be taken to the federal circuit courts or the Supreme Court. | Final judicial determination, which is often the end of the legal road. |
The table above provides a clear view of the multi-step process that individuals must endure. Each phase is filled with its own little twists and intimidating delays, which collectively compound the costs—both personal and financial—of the deportation process.
The Human Impact and Broader Societal Implications
Beyond the legal and financial aspects, the human toll of deportation cannot be understated. The process, with all its complicated pieces and overwhelming challenges, affects real lives—often separating families and disrupting communities.
Family Separation and Community Disruption
When individuals are removed from the U.S., the repercussions are felt immediately within their communities. Families are torn apart, children are left without parental guidance, and communities lose the contributions of long-time residents. Such separations often have long-term detrimental effects that ripple through generations.
Social and Economic Costs
The social costs extend to the economic sphere as well. Removed individuals are often part of the labor force, and their sudden absence can leave gaps in both local economies and key industries. Consider the following points:
- Loss of experienced workers: Communities suffer from a depletion of skilled and experienced workers.
- Economic instability: Sudden deportations can disrupt local markets and lead to reduced consumer spending.
- Increased administrative expenses: The cost of processing, detaining, and legally challenging deportation orders adds up for taxpayers.
When evaluating the deportation process, it is important to consider not only the legal aspects but also these broader human and economic impacts.
Political and Policy Debates Surrounding Deportation
The U.S. immigration system not only involves legal procedures but also represents a deeply political issue. Over the past decades, immigration reform has been a recurring topic in political debates, yet true comprehensive reform has remained elusive.
Historical Policy Shifts and Political Pressures
Every presidential administration brings its own perspective on how best to handle immigration. For instance, recent administrations have shown tendencies to expand removal criteria and enlist additional federal agencies in the process. This trend reflects a shifting landscape that many describe as “the sands shifting underneath our feet” in both legal and political terms.
The Role of Congress in Reform
Despite the clear need for updating an overwhelmed system, legislative reform has repeatedly stalled in Congress. Even with promising bipartisan initiatives emerging at times, political pressures and electoral strategies have often derailed potential solutions. The public debate is frequently loaded with issues such as border security, humanitarian obligations, and the economic implications of immigration policy.
Key Considerations for Future Legislation
- Modernization of immigration courts: Investing in more judges and staff to reduce backlogs.
- Improved detention standards: Ensuring humane and cost-effective treatment of detainees.
- Balanced enforcement policies: Integrating law enforcement with community-based support systems to mitigate societal disruption.
The challenges facing the U.S. immigration system are on many levels—legal, financial, and social. Addressing these challenges calls for a well-rounded approach that considers the fine shades of each issue.
Comparative Perspectives: International Approaches to Deportation
To fully appreciate the complexities and costs of the U.S. deportation process, it can be helpful to consider how other countries manage similar issues. When we compare practices internationally, we find varied approaches that balance enforcement with humanitarian considerations.
Models from Europe and Beyond
Several European countries have reformed their immigration systems to streamline the deportation process while protecting individual rights. These models often include:
- More robust legal aid systems to ensure access to fair hearings
- Quicker processing times in immigration courts through increased staffing
- Alternatives to detention, such as electronic monitoring and community-based supervision
Some nations have even integrated community support programs that help maintain family unity and employment stability until a final decision is made. These alternative methods represent a balance between strict law enforcement and the humane treatment of migrants—a balance that the U.S. currently struggles to achieve.
Lessons for U.S. Policy Makers
As our national debate on immigration continues, policy makers could take cues from these international examples. By embracing a more measured approach—one that values both security and compassion—the United States might find ways to reduce the overwhelming financial and human toll of its current system.
The Future of Deportation Reform: A Call for Comprehensive Change
As we look forward, it is clear that maintaining the status quo in the deportation process is neither sustainable nor just. The system is replete with confusing bits and off-putting hurdles that not only strain legal resources but also deeply impact the lives of millions of individuals.
Key Areas Needing Immediate Attention
There are several super important areas where change is desperately needed. These include:
- Case backlogs in immigration courts: Addressing these delays by increasing resources and streamlining procedures would reduce the nerve-racking wait times for hearings.
- Detention practices: Reforming detention standards and exploring alternatives to confinement can help lower costs and reduce the adverse impact on family life.
- Legal representation: Ensuring that individuals have access to competent legal counsel could fundamentally improve the fairness of the deportation process.
These initiatives require thoughtful legislative action and a willingness to challenge entrenched bureaucratic practices. The system is clearly overloaded with outdated policies that no longer reflect modern realities, and reform is not only critical—it is essential for the rule of law and the protection of individual rights.
Engaging Stakeholders and Building Consensus
Meaningful reform must be a collaborative process that involves a myriad of stakeholders. These include:
- Law enforcement agencies: To balance enforcement with humane treatment and legal due process.
- Legal experts and advocates: To ensure that every individual’s rights are protected, especially during the appeals process.
- Community organizations: To offer support for those affected by deportations and to build bridges between communities and law enforcement.
- Policy makers: To drive Congressional action that transforms outdated processes into a system fit for the 21st century.
These groups each play a role in shaping an immigration system that can handle modern migration challenges without sacrificing fairness or efficiency.
Concluding Thoughts: A System at a Crossroads
The U.S. deportation process embodies a series of twisted issues that span legal, financial, and humanitarian realms. While on the surface it is a set procedure—from identifying removable individuals, through detention, hearings, and ultimately removal—the deeper analysis reveals a labyrinth of problematic details.
It is clear that the current system, with its significant financial burdens and human costs, is in desperate need of reform. The complex pieces—from the role of multiple federal agencies to the overwhelming backlog in immigration courts—are not isolated incidents but interconnected challenges that require comprehensive, bipartisan solutions.
One cannot ignore the far-reaching implications of our immigration policies, which affect both the lives of individuals and the broader socio-economic fabric of our nation. In a process that has long been subject to political manipulation and shifting legislative tides, the need for stable, fair, and sustainable policies has never been more critical.
As our society continues to grapple with these issues, it is important to recognize that deportation is not merely a legal procedure—it is a human story, loaded with both emotion and consequence. The path forward must balance security needs with compassion, ensuring that every individual is treated with dignity and fairness under the law.
Ultimately, it is up to our lawmakers, legal experts, and community leaders to work together to update the system. Whether it’s increasing resources for the immigration courts, rethinking detention practices, or ensuring due process through improved legal representation, the steps we take today will shape the future of our immigration policy and set a precedent for generations to come.
The Pressing Need for Comprehensive Immigration Reform
In closing, the U.S. immigration system—especially the deportation process—is a contentious yet indispensable subject for discussion. The steps we take toward reform must address the fine points and subtle parts that burden the system:
- Modernization and Investment: Adequate funding for immigration courts and detention facilities will help in shortening case delays and reducing taxpayer expenses.
- Legislative Action: Congress must chart a course that balances strict law enforcement with fairness, modernizing policies to meet contemporary challenges.
- Ensuring Due Process: Upholding the legal rights of every individual through improved access to legal counsel and fair hearings is non-negotiable.
- Community Engagement: Creating bonds between law enforcement and communities can help alleviate the social disruption caused by rapid deportations and separations.
These steps, while challenging, are essential for ensuring that a system as monumental as U.S. immigration reform can adapt to the evolving realities of modern society. The twists and turns of the current process illustrate that our approach to immigration needs a complete overhaul—one that is equitable, efficient, and humane.
Only by recognizing the interwoven legal, financial, and human dimensions of deportation can we begin to address the overwhelming scale of the challenges ahead. Whether you are a legal scholar, a policy maker, or a concerned citizen, it is super important to take a closer look at the costs and consequences of our current practices. The future of immigration law depends on our ability to work through these issues together, challenging cumbersome traditions and putting forward solutions that respect both the law and human dignity.
A Final Word on the Path Forward
In our opinion, the U.S. deportation process serves as a mirror reflecting broader societal challenges. It presents a scenario where policies enacted under various administrations pile one confusing step on top of another—from identification and arrest, detention and legal processing, to the deep impacts on communities and families. The system, as it stands, is overwhelmed and in urgent need of legislative and administrative reform.
We must figure a path that does not sacrifice individual rights at the altar of enforcement efficiency. Instead, we need to create a legal framework that is flexible enough to adapt to modern realities, yet firm in upholding the principles of due process and fairness.
This discussion, far from being a mere technical breakdown, is ultimately about shaping a future where immigration policy and deportation practices are fully aligned with both our constitutional values and the changing landscape of global migration. The road ahead will be challenging, full of nerve-racking decisions and tangled issues, but it also offers a transformative opportunity to reform a system long overdue for change.
Let this be a call to action: policymakers, legal experts, and community advocates must not shy away from the task of revamping our immigration policies. By embracing a holistic approach that meticulously considers every step of the deportation process—from border control to courtroom appeals—we can build a system that meets the needs of today while setting a solid foundation for tomorrow.
In sum, solving the issues inherent in the current deportation process is not just a matter of legal procedure or cost efficiency—it is a matter of justice and humanity. As we embark on this journey of reform and renewal, every stakeholder must work hand in hand to ensure that our nation’s immigration laws are not only effective but also just and compassionate.
Originally Post From https://www.kawc.org/npr-news/2025-04-07/how-does-deportation-work-and-how-much-does-it-cost-we-break-it-down
Read more about this topic at
Americans’ Views of Deportations
Deciphering deportation practices across the Global North